¶ M2M Authorization
M2M (Machine to Machine) authorization is an authorization between applications without user participation. When you want to partially open your business API to others, such as your outsourcer, the outsourcer needs to perform M2M authorization before you can access your business API. Suppose your company wants to develop a large-screen display of some data, and several outsourcers participate in it. You want to authorize access to certain non-core data APIs to outsourcers so that the outsourcers can complete this part of the non-core development. At this time, M2M authorization is required, because no user participation is required in this process, we only need to determine which outsourcer the visitor is and what interface access he has.
The following is the architecture diagram of this scenario. The outsourcer first goes to Authing to obtain the Access Token, and then carries the Access Token to access the API interface of the company's services:

¶ Privilege management and assignment
Create an application in Authing called "Big Screen Display".

Define some resources under the "big screen display" application, and each resource corresponds to the actual resource in the "big screen display" application. Here we add some resources, including user-growth, customer, announcement, and revenue. The name of these resources is API scope.





After defining the resources and operations, add a programmatic access account for the application. The programmatic access account is the caller of the API interface of the current application. The program access account has a pair of AK and SK, which are used by the outsourcer to call the "big screen display" application interface. We can hand over AK and SK with different privileges to different outsourcers, so that they have different privileges and can access different APIs.

Create two programming access accounts, fill in the AccessToken expiration time and remarks, and click OK.


If the program access account is deleted, the caller will lose the access.
¶ Access Token expire time
When you create a programmatic access account, you need to specify the AccessToken expiration time. Authing uses the RS256 signature algorithm when issuing the AccessToken to ensure that the AccessToken will not be tampered with.
Token signature is a part of JWT. For more information, please refer to JWT Interpretation and Usage.
RS256 is an asymmetric signature algorithm. Authing holds the private key to sign the Token, and consumers of JWT use the public key to verify the signature. The RS256 signature algorithm has the following advantages:
- Anyone can use the application public key to verify the signature, and the signer must be Authing.
- There is no risk of private key leakage. If you use HS256 but leak the application key, you need to refresh the key and redeploy all APIs. For more details on signature issues, please refer to Verify the Token. We have just created two programming access accounts, which will need to be handed over to outsourcers in the future.

Next we need to give them resource privileges. On the Resource Authorization tab, click Add.

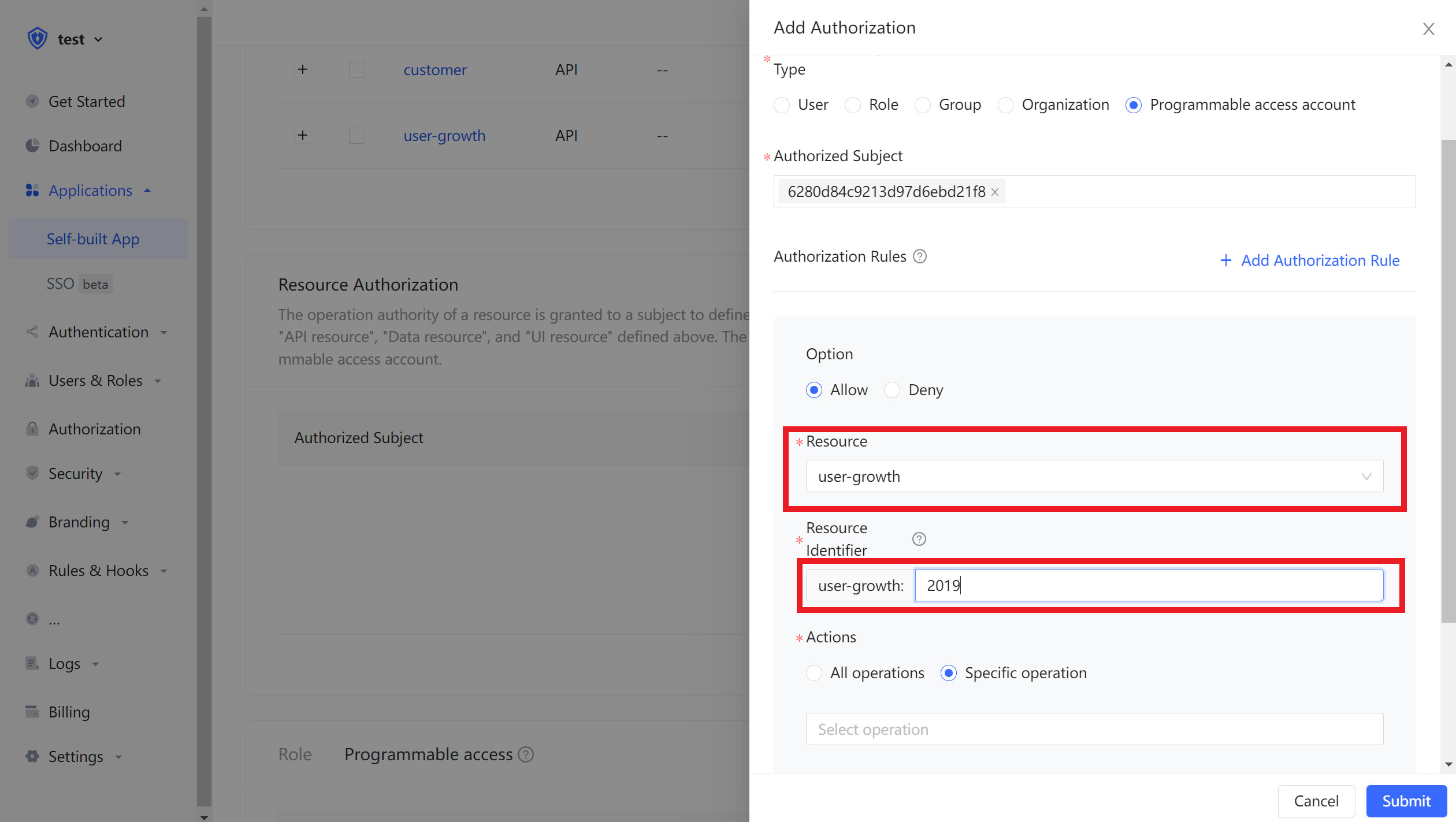
In the authorized subject type, select programming access account, and then select the programming access account of the outsourcing company A.

In the authorization rules, select announcement information as the resource type, fill * in resource identifier to authorize all announcement resources, then choose specific operation and then select the announce:read operation. At last, click the confirm button. The function of this rule is to authorize the outsourcing company A to read access to all announcement information resources.

Next, we add privileges for outsourcing company B. First select the programming access account of outsourcing company B.

Then, we need to add three rules:
Authorize all operation privileges of user growth data in 2019 to outsourcer B. Click Add Authorization Rule at the top right to add multiple rules.
- Authorize the creation, reading, and modification permissions of all revenue records to outsourcer B.

- Authorize the access to read all customer records to outsourcer B.

At this point, the administrator's access management operations are all over. Below we will conduct M2M authorization best practices from the perspective of the caller and the resource side.
¶ Get permissioned Access Token
The OIDC authorization framework provides many authorization modes. In this scenario, obtaining user growth information belongs to M2M (machine-to-machine) authorization. The caller uses his own identity to access the API interface of the resource server without user participation. The OIDC ClientCredentials mode is required here. Through the OIDC ClientCredentials authorization mode, the caller needs to provide Authing with his ClientCredentials (that is, the Key and Secret of the programmatic access account) and the required privilege scope (that is, the resource identifier) to directly obtain an AccessToken with the API access

- The caller sends the Key and Secret of the programmatic access account and the required permission object scope to Authing.
- Authing verifies the programmatic access account Key and Secret.
- Authing checks the scope permission items according to the permission rules configured by the administrator, and issues an AccessToken with the permission to access resources. The denied permission scope will not appear in the AccessToken.
- The caller carries the AccessToken to access the resource server.
- The resource server returns the protected resource. In order for the caller to be able to access the protected API interface, it must first obtain an AccessToken with the privileges. To do this, the caller needs to send a POST request to the following address. Request URL:
https://{APP_DOMAIN_NAME}.authing.cn/oidc/tokenParameters:
| Parameter name | description |
|---|---|
| grant_type | Filled with client_credentials. |
| client_id | Programmatic access account Key |
| client_secret | Programmatic access account secret |
| scope | Requested object scope. The form is resource identifier:resource operation. Use space to seperate. |
Respond:
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCIsImtpZCI6IjF6aXlIVG15M184MDRDOU1jUENHVERmYWJCNThBNENlZG9Wa3VweXdVeU0ifQ.eyJqdGkiOiJ2S1ZGV3FKemltTm5MSTlYZy0zam0iLCJpYXQiOjE2MTI1MDA2OTgsImV4cCI6MTYxMjUwNDI5OCwic2NvcGUiOiJib29rIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9zdGVhbS10YWxrLmF1dGhpbmcuY24vb2lkYyIsImF1ZCI6IjYwMWJmMzVhY2E1ZDM4NzVjNDY3NDgyYyIsImF6cCI6IjYwMTkzYzYxMGY5MTE3ZTdjYjA0OTE1OSJ9.DS0l6zdlr_bGLqmDQRxvHUL4fmyLS5je6bqUCSSo06OIWSfcDZMZAqH5aYXP7Hzm4SiT6sfOCP_IiPSOxJPgFPYAmQTPSvJ5e6zs9jNeZyep_O6NWjlOGbDirskZE1pSZO_16ceiFr3jprSp13ff6O6Fa9YkY-8b_L3ouDqKhtb_4051pWZif-VzgXSkmvflTmqauJul9b5PzaeGWL-PKOrHrUiHjJwf9wqtR-3C8voFmi9pmxrUJYGSJoxwcxxSEceUY3d9oJU3v7e6FOnT_EMxfQCrAgzXR21bOitsAutOVXg1N9H0QJiNBESorCcj6yi1fVePTeDI5nY6xj9oDw",
"expires_in": 3600,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"scope": "book",
"rejected_scope": "message table"
}
Sample code:
const axios = require("axios").default;
const options = {
method: "POST",
url: "https://{应用域名}.authing.cn/oidc/token",
headers: { "content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" },
data: {
grant_type: "client_credentials",
client_id: "{编程访问账号 Key}",
client_secret: "{编程访问账号 Secret}",
scope: "{权限项目,空格分隔}"
}
};
axios
.request(options)
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response.data);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.error(error);
});
We only authorize outsourcing company A to read the announcement information. If outsourcing company A requests authorization with other scopes, for example: announce:read announce:update revenue:read customer user-growth:read. Authing will grant to give any privilege except announce:read. The following is the result returned when outsourcing company A requests authorization. The denied privileges are in rejected_scope.

The AccessToken information only contains the scope which you have privilege:

Let’s take a look at the authorization of outsourcer B. If outsourcer B wants to request the following scope: user-growth:2020:read user-growth:2019:_ user-growth:2019:read revenue:create revenue:_:read customer:read Authing will return:
Authing will return:

It should be noted that the administrator only authorized all permissions for the user growth data in 2019 to the outsourcing company B, so when it requests the scope of the user growth data in 2020, it was denied.
¶ Scope permission item specification
Authing's scope permission items are separated by spaces, and the format of each item is resource identifier:resource operation.
The following are all scope formats supported by Authing:
book:1:read means the read permission of the book resource with number "1"
book:*:read means the read permission of all book resources
book:read means the read permission of all book resources
book:*:* means all operation permissions for all book resources
book:* means all operation permissions for all book resources
book means all operation permissions for all book resources
*:*:* means all operation permissions for all resources
*:* means all operation permissions for all resources
* Means all operation permissions for all resources
¶ Add API authentication interceptor
After Authing defines the API, you need to add an API authentication interceptor to your actual business API interface. For protected resources, only visitors who carry a valid AccessToken and have the required permissions are allowed. The code example is as follows:
var express = require("express");
var app = express();
var jwt = require("express-jwt");
var jwks = require("jwks-rsa");
var port = process.env.PORT || 8080;
var jwtCheck = jwt({
secret: jwks.expressJwtSecret({
cache: true,
rateLimit: true,
jwksRequestsPerMinute: 5,
jwksUri: "https://{应用域名}.authing.cn/oidc/.well-known/jwks.json"
}),
audience: "{编程访问账号 ID}",
issuer: "https://{应用域名}.authing.cn/oidc",
algorithms: ["RS256"]
});
// 检验 AccessToken 合法性
app.use(jwtCheck);
app.post("/article", function(req, res) {
// 检验 AccessToken 是否具备所需要的权限项目
if (!req.user.scope.split(" ").incldues("write:article")) {
return res.status(401).json({ code: 401, message: "Unauthorized" });
}
res.send("Secured Resource");
});
app.listen(port);
For other content about Token validation, please refer to how to validate user token.
